Why does Friends of the Kaw fight Dredging?
What does a dredge look like?
What should boaters know about dredging?
How does dredging threaten economic development?
How does dredging threaten water supplies?
What is dredging?
How long has dredging been happening?
How does dredging damage the river?
How does dredging cause channel widening?
How does dredging cause “bank armoring?”
Does dredging affect water quality for people and animals?
What needs to be done to make a responsible decision about the river?
How should we manage the river?
Why does Friends of the Kaw fight dredging? Friends of the Kaw views dredging as the greatest imminent threat to the health and benefits of the Kansas River for present and future generations. Back to Top
What does a dredge look like? A dredge (picture right) is a large and loud machine that sucks sand from the river bottom. Dredges are typically maintained on the river on pontoons, and run the sand onto shore nearby.  Back to Top
Back to Top
What should boaters know about dredging? Boaters should know that dredging operations cause drastic changes in the river bed through the removal of sand. This removal causes sand bars to disappear and reduces recreational opportunity. The equipment also creates an increased hazard to boaters, such as cables just under the surface of the water. Boaters should be cautious near dredges. Back to Top
How does dredging threaten economic development? The Kansas River is a declared national water trail and provides drinking water to hundreds of thousands of individuals. Bed degradation threatens this valuable natural resource as a drinking water supply, and as a priceless outdoor recreation area. Back to Top
How does dredging threaten water supplies? Increased degradation of the river bed causes lowering of the water table and river bed. This can cause water supply intakes to run dry as the water level decreases below the level of the intakes. This has already happened multiple times on the Missouri River. Back to Top
What is dredging? Dredging is the removal of sediment from a stream bed. The dredge either scoops or sucks material from the bed of the channel, causing a depression to be scoured into the river bed. Back to Top
How long has dredging been happening? The Kansas River has been commercially mined for sand and gravel since the early 1900’s. In recent years, however, studies have documented that dredging activities have caused significant damage to the Kaw’s riverbed, to habitat in and along the river, and to water quality. These studies resulted in the Corps of Engineers closing some stretches of the river to further dredging. Back to Top
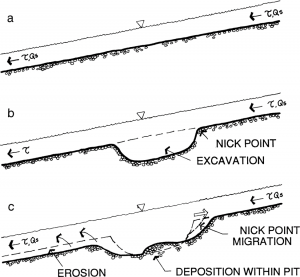
How does dredging damage the river? The upstream edge of the “dredge hole” is eroded upstream by moving water. As water flows into the dredge hole, it loses velocity, causing some of the fine materials it carries to deposit in the bottom of the pit. As water continues to flow out of the dredge hole it once again increases velocity, picking up bed sediments and erosion downstream from the dredge hole (see the image below). Back to Top
How does dredging cause channel widening? The process described above causes upstream and downstream erosion, bed degradation, and channel instability. Lowering the river bed causes banks that were once stable to slump into the river, resulting in an overall widening of the channel. This widening causes loss of streamside vegetation, loss of valuable farmland, and damage to infrastructure. Back to Top
How does dredging cause “bank armoring”? Channel widening may also result in costly or illegal bank armoring, as landowners seek to prevent further losses of land. Those that live along the river bank where this process occurs often are forced to use costly or illegal measures to armor the bank and prevent it from washing away. Back to Top
Does dredging affect water quality for people and animals? Dredging alters the physical habitat crucial to many native fish species. As sand is suctioned from the channel, bottom sediments are re-suspended in the water column, increasing turbidity downstream. These sediments are very likely associated with pollutants such as PCBs, pesticides, and herbicides such as atrazine that tend to bind to sediment particles. There is also a potential for a significant increase in the cost of drinking water treatment downstream as additional sediment and pollutant leads have to be removed. Back to Top
What needs to be done to make a responsible decision about the river? We will need to continue sampling at higher water levels, and continue monitoring the behavior of channels near dredge holes. More information is needed to determine how quickly migration happens, how the nick point migrates upstream, and to answer many other questions.Back to Top
How should we manage the river? It is important to manage the river for channel stability, infrastructure, water quality, recreation, and habitat. There are other alternatives worth exploring like restricting in-channel mining and moving sand mining operations to strategically placed pit mines in the flood plain. More research is needed to determine a way to sustainably mine the Kansas River valley for sand. Back to Top